Electrical
power distribution is the last stage in the delivery of electric power. It
carries electricity from the transmission system to the individual consumers.
The primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage to distribution
transformers.
The
distribution networks of concern in this stage are 11KV lines or feeders downstream
of the 33KV substations. Each 11KV feeder, which come from the 33KV
substation branches further into several subsidiary 11KV feeders to carry
power close to the load points, where it is further stepped down to either 230V
or 414V.
Normally for
fault detection, we have circuit breakers i.e. one circuit breaker for every
main 11KV feeder at the 33KV substations, but these circuit breakers are
provided as a means of protection to completely isolate the downstream network
in the event of a fault. For quick fault detection, isolation of faulty region
and restoration of supply to the maximum outage area, we need to have a system
that can achieve a finer resolution.
In the event
of a fault on any feeder section downstream, the circuit breaker at the 33KV
substation trips, as a result, we have a blackout over a large section of the
distribution network. If we can precisely identify the faulty segment, we can
reduce the blackout area, by re-routing the power to the healthy feeder
segments through the operation of sectionalizing switches, placed at strategic
locations in various feeder segments.
The lack of
information at the 33KV substations of the loading and health status of 11KV/415V distribution transformers and associated feeders is one of the main
causes of inefficient power distribution.
When we have no monitoring, overloading occurs, which results in low
voltage at the customer end, and this increases the risk of frequent breakdowns
of the transformers and feeders.
To prevent
the above problems from occurring in a power distribution network, we need to
have an automated electrical power distribution system.
You can also read: How to integrate PLC into a Control System
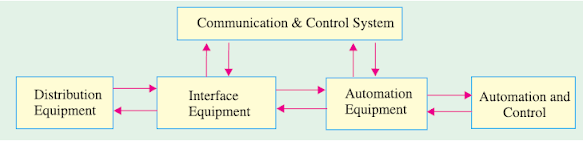
How Electrical Power Distribution Automated System work
To enhance
the electrical power distribution reliability, sectionalizing switches are
provided along the way of primary feeders. Thus, by adding fault detecting
relays to the sectionalizing switches along with circuit breaker and protective
relays at the distribution substations, the system is capable of determining
fault sections. To reduce the service disruption area in the case of power
failure, normally open (NO) sectionalizing switches called as route switches
are used for supply restoration process. The operation of these switches is
controlled from the control center through the Remote Terminal Units (RTU).
In a power
distribution automation system, the various quantities e.g. current, voltage,
switch status, temperature and oil level are recorded in the field at the
distribution transformers and feeders, using a data acquisition device called
Remote Terminal Unit. These quantities re transmitted on-line to the base
station through a communication media. The acquired data is processed at the
base station for display at multiple computers through a Graphic user interface
(GUI).
In the event
of a system quantity crossing a pre-defined threshold, an alarm is generated
for operator intervention. Any control action, for opening or closing of the
switch or circuit breaker is initiated by the operator and transmitted from the
33KV base stations through the communication channel to the remote terminal
unit associated with the corresponding switch or CB. The desired switching
takes place and the action is confirmed by the operator.
All these
distribution automation functions of data collection, data transmission, data
monitoring, data processing, man-machine interface etc. are realized using an
integrated distribution SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
system.
Don't miss out on key updates, join our newsletter list here.
The
implementation of SCADA system in any electric utility involves the
installation of the following units:
- Sectionalizing Switches
- Remote Terminal Units
- Data Acquisition System
- Communication Interface
- Control PC
No comments:
Post a Comment