The major principles employed for liquid flowmeter calibration are:
- In-situ calibration methods {Insertion-point velocity and Dilution gauging/tracer technique}
- Laboratory methods {master meter, volumetric gravimetric and pipe prover}
In-situ calibration methods
Insertion-point velocity – this is one of the simplest methods
of in-situ flowmeter calibration. It utilizes point-velocity measuring devices
where the calibration device selected is positioned in the flow stream adjacent
to the flowmeter being calibrated, such that the mean flow velocity can be
measured. In difficult situations a flow traverse can be carried out to
establish the flow profile and mean flow velocity.
Dilution gauging/Tracer method – this method can be applied to closed-pipe and open-channel flowmeter calibration. An appropriate tracer (chemical or radioactive) is injected at an accurately measured constant rate and samples are taken from the flow stream at a point downstream of the injection point where complete mixing of the injected tracer will have taken place. By measuring the tracer concentration in the samples the tracer dilution can be determined and from this dilution and the injection rate the volumetric flow can be calculated.
 |
Figure 1.0 Dilution gauging by tracer injection
Alternatively
a pulse of tracer material may be added to the flow stream and the time taken
for the tracer to travel a known distance and reach a maximum concentration is
a measure of the flow velocity.
Related: Instruments Errors and Calibration
Laboratory calibration methods
Master meter – for this method a meter of known
accuracy is used as a calibration standard. The meter to be calibrated and the
master meter are connected in series and are then subjected to the same flow
regime. Note that, to ensure consistent accurate calibration the master meter
itself must be subject to periodic calibration.
Volumetric method – in this technique, the flow of
liquid through the meter being calibrated is diverted into a tank of known
volume. When full, this known volume can be compared with integrated quantity
registered by the flowmeter being calibrated.
Gravimetric method – where the flow of liquid through the meter being calibrated is diverted into a vessel that can be weighed either continuously or after a predetermined time, the weight of the liquid is compared with the registered reading of the flowmeter being calibrated.
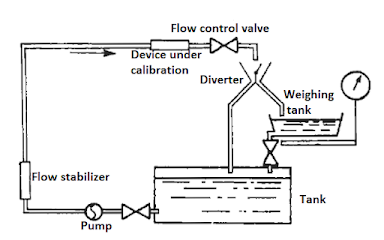 |
| Figure 1.1 calibrating a flowmeter by weighing |
Pipe prover – this device also known as a meter prover, consists of a U-shaped length of pipe and a piston or elastic sphere. The flowmeter to be calibrated is installed on the inlet to the prover and the sphere is forced to travel to the length of the pipe by the flowing liquid. Switches are inserted near both ends of the pipe and operate when the spheres passes them. The swept volume of the pipe between the two switches is determined by initial calibration and this known volume is compared with that registered by the flowmeter during calibration.
No comments:
Post a Comment