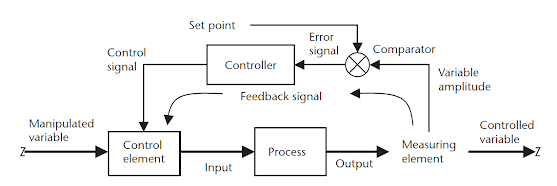
Control loop consists of all the key elements necessary
to move the final control elements. We have different types of final control
elements like the Valves, Motors, Fans etc. The final control elements makes it
possible to keep controlled variable on target.
Related: The Transition from Relay Control Systems to PLC Systems
Don't miss out on key updates, join our newsletter list here.
Let's Consider the following diagram:
The Process measuring elements sends a signal to the
controller. In this case the level transmitter sends the signal of the measured process variable to the level controller. At the same time the already determined set point is compared with
the signal coming from the measuring device.
The error detector makes a comparison
between the signal from the process and the set point signal. If there is a
difference between this, an error signal is sent to the control logic that
changes the position of final control device (In our case; it is the control valve). The change in the Final control
device will cause a change in the process. This process will continue until the
set point is maintained.
Key elements of a control loop includes:
- The measuring device/Process measurement instrument
- Controller
- Final Control device, in this case, the control valve
Common terms used:
- Process Variable
- Manipulated Variable
- Controller Error
- Set point
Explaining the terms in more details:
Measuring device: This is the instrument that measures the physical
quantity. This can be the temperature, level, flow rate, Pressure etc. It then
converts this into a signal that can be easily picked up by the controller.
Process Variable: This is the process value or the process parameter
i.e. the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is
being monitored or controlled. The current level is the process variable while
the desired level is known as the set point.
Process Control: The automatic control of certain process variables
to hold them within given limits.
Set point: The reference value for a controlled variable in a
process control loop.
Controller: The element in a process control loop that evaluates
any error of the measured variable and initiates corrective action by changing
the manipulated variable.
Controller Error: The difference in value between a measured signal
and a set point.
Final Control Device (Actuator): A device that performs an action
on one of the input variables of a process according to a signal received from
the controller.
Manipulated Variable: The variable controlled by
an actuator to correct for changes in the measured variable. Related: The Transition from Relay Control Systems to PLC Systems
Don't miss out on key updates, join our newsletter list here.