Programmable logic controllers (PLC) play an
important role in automation sector. Various industries like Food &
Beverage, Chemical, Petrochemical, Power generation etc. use PLC.
Functions of each component:
CPU – This the unit that contains microprocessors
We have several types of PLC designs:
Compact PLC: This is built by several modules within a single
case. The I/O capabilities are decided by the manufacturer and not the user.
Modular PLC: This is built with several components that are
plugged into a common rack or bus with extended I/O capabilities. It contains
power supply module, CPU and other I/O modules that are plugged together in the
same rack, which are from the same manufacturers or from different
manufacturers.
Soft PLC: This is an advanced PLC system that consists of
compact, rack mounted components such as power supplies, I/O modules and a CPU
which embeds a powerful PLC Control software.
Programming Languages of PLC
There are several programming languages used to
write programs in a PLC. They include but not limited:
- Ladder Diagram
- Instruction List
- Functional Block Diagram
- Sequential Function Chart
- Structured Text
So what are some of the components that make up a Programmable Logic
Controllers?
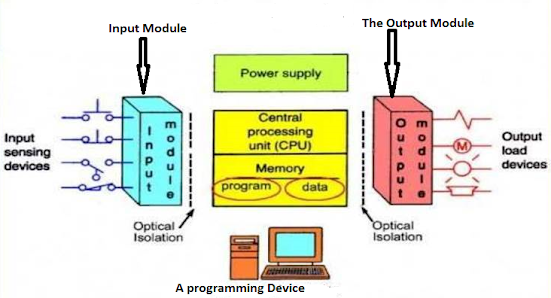 |
| PLC System |
Functions of each component:
CPU – This the unit that contains microprocessors
Input and Output Sections – This is where the processor
receives information from external devices and communicates information to
external devices.
Power Supply Unit– It converts the Main AC voltage
to low DC voltage.
Programming device – Used to enter the required
program into the memory of the processor.
Memory Unit – This is where the program is stored
that is used to control actions.
The Operation of a PLC
Check the input status: First
the PLC takes a look at each I/O to determine if it is on or off.
Execute Program: Next the PLC executes
the program one instruction at a time.
Update output status: Finally
the PLC updates the outputs. It updates the outputs based on which inputs were
on during the first step.
Advantages of PLC:
- More flexibility
- Lower cost
- Increased reliability
- Faster response
- Easier to troubleshoot
- Communication capability
- Remote control capability
Disadvantages:
- They can render some jobs redundant
- They have a high initial cost
- If a Programmable logic controller stops, then the production stops
Industrial Applications of PLCs
- Food and Beverage industry
- Gas and Water Filling Stations
- Power Sector
- Bottling Plants
You can also read:
Some of the Top PLC Brands in the
world include:
Don't miss out on our Control and Automation articles, join our Newsletter list here.

No comments:
Post a Comment