A process is
a sequence of events designed to control the flow of materials through a number
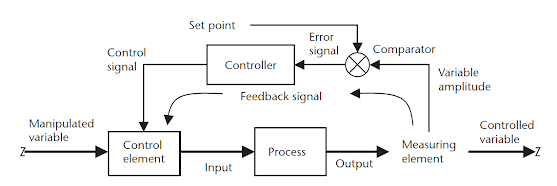
of steps in a plant to produce a final product. To get a better understanding of a process control system, we can have a look at the following diagram
showing elements in a continuous control process with a feedback loop.
Measurement is the determination of the physical amplitude of a parameter of a material. The measurement value must be consistent and repeatable.
Sensors are used for the measurement of the physical parameters. Sensors are devices that convert the physical parameters repeatedly and reliably into a form that can be used in the control system. For example, you will find sensors being used to convert Pressure, Temperature, Flow, Level etc. into an electrical signal that is well understood by the system.
Error Detection is the determination of the difference between the amplitude of the measured variable and a desired set reference point or normally called set point. Any difference between the two is an error signal, which is amplified and conditioned to drive a control element. The reference point is usually stored in the memory of the controller.
The Controller is a microprocessor-based system that can determine the next step to be taken in a sequential process, or evaluate the error signal in a continuous process control system to determine what action is to be taken.
The controller can condition the signal, i.e. correct the signal for temperature effects or non-linearity in the sensor. The controller also has the parameters of the process input control element, and conditions the error sign to drive the final element.
You can also read:
The control element is the device that controls the incoming material to the process. Typically the element is a flow control element, and can have On/Off characteristics or can provide linear control with drive. The control element is used to adjust the input to the process, bringing the output variable to the value of the set point.
Don't miss out on key updates, join our newsletter list here.
Note that,
the process can be a simple one, with a few steps, or a complex sequence of
events with a large number of interrelated variables. The examples in the above
diagram show single steps that may occur in a process.
Measurement is the determination of the physical amplitude of a parameter of a material. The measurement value must be consistent and repeatable.
Sensors are used for the measurement of the physical parameters. Sensors are devices that convert the physical parameters repeatedly and reliably into a form that can be used in the control system. For example, you will find sensors being used to convert Pressure, Temperature, Flow, Level etc. into an electrical signal that is well understood by the system.
Error Detection is the determination of the difference between the amplitude of the measured variable and a desired set reference point or normally called set point. Any difference between the two is an error signal, which is amplified and conditioned to drive a control element. The reference point is usually stored in the memory of the controller.
The Controller is a microprocessor-based system that can determine the next step to be taken in a sequential process, or evaluate the error signal in a continuous process control system to determine what action is to be taken.
The controller can condition the signal, i.e. correct the signal for temperature effects or non-linearity in the sensor. The controller also has the parameters of the process input control element, and conditions the error sign to drive the final element.
The
controller can monitor several input signals that are sometimes interrelated,
and can drive several control elements simultaneously.
You can also read:
- The Basics of Industrial Instrumentation and Control Systems
- How Smart Sensors are used in Industrial Control
The control element is the device that controls the incoming material to the process. Typically the element is a flow control element, and can have On/Off characteristics or can provide linear control with drive. The control element is used to adjust the input to the process, bringing the output variable to the value of the set point.
In our
figure above, the measuring element consists of a sensor to measure the
physical property of a variable, a transducer to convert the sensor signal into
an electrical signal, and a transmitter to amplify the electrical signal, so
that it can be transmitted without loss.
The control
element has an actuator which changes the electrical signal from the controller
into a signal to operate the valve, and also control the valve. In a closed
loop control system or a feedback loop, the controller has memory and a summing
circuit to compare the set point to the sensed signal, so that it can generate
an error signal.
The
controller then uses the error signal to generate a correctional signal to
control the valve via actuator and the input variable.
No comments:
Post a Comment