Vortex
flowmeters are used to measure the flow of Gases, Vapours and liquids in
completely filled pipes. The measuring principle behind vortex flowmeters is
based on the Karman vortex street.
Advantages of using Vortex Flowmeters
Disadvantages of using Vortex Flowmeters
You can also read:
Industrial Applications of Vortex Flowmeters
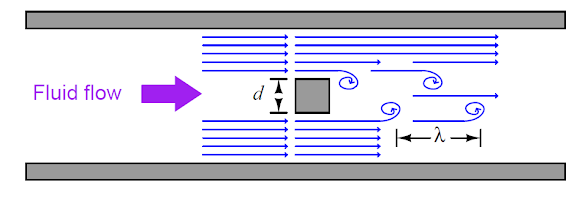
When a fluid moves with a high Reynolds number past a stationary object (a
bluff body) there is tendency for the fluid to form vortices on either side of
the object. Each vortex will form, then detach from the object and continue to
move with the flowing gas or liquid, one side at a time in alternating fashion.
This phenomenon is known as vortex shedding, and the pattern of moving vortices
carried downstream of the stationary object is known as a vortex street.
From the
research that was first done by Vincenc Strouhal then later on, by Theodore Von
Karman, It was established that the distance between the successive vortices
downstream of the stationary object is relatively constant, and directly
proportional to the width of the object, for a wide range of Reynold number
values.
If consider
these vortices as crests of a continuous wave, the distance between vortices
may be represented by the symbol of wavelength ‘’lambda’’ (λ)
d- Object width
λ- Vortex street wavelength
S- Strouhal
number
(λS = d) where S is approximately equal to 0.17
The wavelength (λ) is equivalent to d/0.17
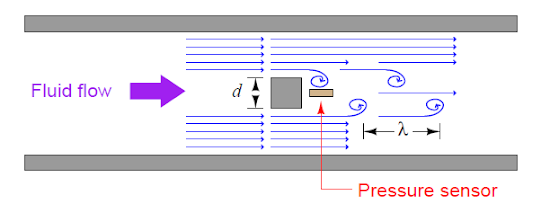
If a
differential Pressure sensor is installed immediately downstream of the
stationary object in such an orientation that it detects the passing vortices
as pressure variations, an alternating signal will be detected.
The
frequency of this alternating pressure signal is directly proportional to fluid
velocity past the object, since the wavelength is constant.
Using the
classic frequency velocity wavelength formula common to all travelling waves; λf = v, and since we know the wavelength from the above, we
may substitute this into this formula.
Velocity (v)
= wavelength (λ) x Frequency (f),
Velocity (v)
= d/0.17 x f
Therefore,
frequency (f) = 0.17v/d
Therefore
the stationary object and pressure sensor installed in the middle of the pipe
section constitute a flowmeter called a Vortex flowmeter; the output frequency
of a vortex flowmeter is linearly proportional to volumetric flow rate.
The pressure
sensors used in vortex flowmeters, are typically piezoelectric crystals.
The
relationship between sensor frequency (f) and volumetric flow rate (Q) may be
expressed as proportionality, with the letter k used to represent the constant
of proportionality for any particular flowmeter:
Therefore, f
= kQ
Where f =
Frequency of output signal (Hz)
Q =Volumetric flow rate (e.g. liters per
second or gallons per second etc.)
K = ‘’K’’ factor of the vortex shedding
flow tube (e.g. pulses per gallon or pulses per a liter)
Each vortex
flowmeter has a ‘’k’’ factor relating to the number of pulses generated per
unit volume passed through the meter.
Counting the
number of pulses over a certain time span yields total fluid volume passed
through the meter over the same time span, making the vortex flowmeter readily
adaptable for totalizing fluid volume.
The direct
proportion between vortex frequency and volumetric flow rate means vortex
flowmeters are linear-responding instruments.
Advantages of using Vortex Flowmeters
Vortex
flowmeters have a wide turn down ratio or a wide range of flow measurement. They
do not require signal characterization to function properly. Since they have no
moving parts, they do not suffer the problems of wear and lubrication facing
turbine or positive displacement meters and can measure erratic flows.
Disadvantages of using Vortex Flowmeters
The
flowmeter may stop working below certain flow rate, known as low cut off. This
is because, at low flow rates i.e. laminar flow (low Reynolds number values),
fluid viscosity becomes sufficient to prevent vortices from forming, causing
the vortex flowmeter to register zero flow even when there may be some flow in
the pipe.
You can also read:
Industrial Applications of Vortex Flowmeters
Vortex flowmeters are used in measurement of saturated steam and
super-heated steam. They are also used in measurement of consumption of industrial gases. You will find them commonly used in Steam boiler monitoring, measurement of consumption in compressed air systems, heat metering in steam & hot water and lastly in SIP and CIP processes in the food, beverage and pharmaceutical industries among other areas not mentioned here.
Don't miss out on key updates, join our newsletter list here.
No comments:
Post a Comment